Most optical cable jackets considered for use in space flight are extruded Teflon or Tefzel. Materials being used for loose tube buffers are Teflon, Tefzel, Kynar (PVDF) or Hytrel. Tight buffer choices are silicone, Teflon and Tefzel. Strength members can be Teflon impregnated fiberglass or Kevlar (Aramid). The options for coatings are acrylates or polyimides with or without an amorphous carbon undercoating, which provides hermeticity. Properties of these materials are outlined in Table 1.
Table 1. Materials Used in Flight Grade Fiber Optic Cable*
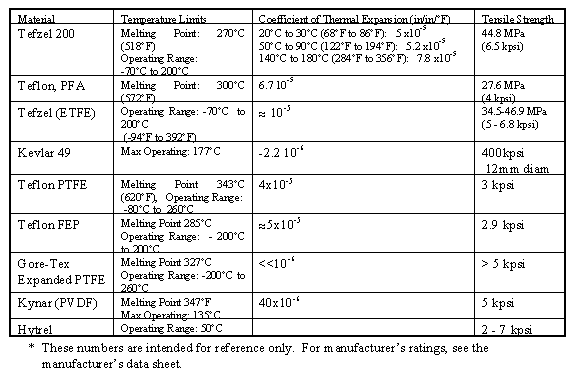
It is interesting to note that the coefficient of thermal expansion for Kevlar is negative, which means that as the temperature increases the material tends to contract rather than expand. The other materials in Table 1 have positive CTE’s. Though no negative impact on performance has been reported by users of flight grade cable with Kevlar strength members, the behavior of the coating material with temperature causes an increase in loss as the temperature is reduced. This is why it is critical to characterize and life test optical fiber with an emphasis on the low end of the rated temperature range.
Table of Contents
Next Section: Shrinking Cable Components